Insecure transmission of sensitive information in Activity
 |
CRITICAL | ||
| Detection method | DAST SENSITIVE INFO |
Description
An application puts sensitive information into an implicit Intent to launch an Activity. This can lead to interception of information by external applications.
Interprocess communication (IPC) on Android is conducted using a special object—Intent. Parameters of Intent handlers are set in the main file of the application manifest - AndroidManifest.xml or, in case of dynamic BroadcastReceivers, in the application's code. If an implicit Intent is used, i.e. an Intent that does not specify a component; instead, it generally defines an action to be conducted, and lets the system determine which of the available components is best to run for that Intent. For example, if there is a need to display a place on a map, the implicit Intent object can request another application, which has such feature, to provide this information. Data in such messages could be compromised. Moreover, malicious applications could use mechanisms of delegation of process control, such as implicit calls to application components or objects like PendingIntent, for interception of control and fishing attacks.
The following object types are dangerous: Activity, Service, BroadcastReceiver and ContentProvider, because they are open to communication with other applications and don't belong to system Android calls (such as android.intent.action.MAIN). BroadcastReceiver is, by default, open to interaction with other applications, so the interception of control or of an Intent with confidential information is possible.
Recommendations
Don't include sensitive information into parameters when using implicit Intents (when a user defines what application will handle a message).
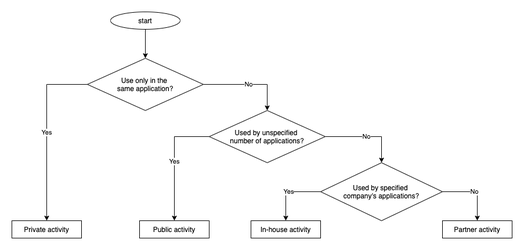
Risks from using an Activity and corresponding countermeasures vary depending on the ways this Activity is used. We have classified 4 types of Activities based on how the Activity is used. To find out which type of Activity you are supposed to create, follow through the table and chart below.
|
Type of Activity |
Description |
|
Private activity |
An activity that cannot be launched by another application, and therefore is the safest one. |
|
Public activity |
An activity that can be used by an unspecified large number of applications. |
|
Partner activity |
An activity that can only be used by specific applications created by trusted partner companies. There is a special list of such applications. |
|
In-house activity |
An activity that can only be used by other applications of the same developer. |
Creating and using a public Activity
As an example we will follow the process of creation of a Public Activity and its usage.
Public Activity is an Activity that can be used by any external application. It is worth mentioning that:
Public Activitycan receive anIntentfrom a malicious application- A malicious application can receive an
Intentsent to apublic Activityand/or read its data
Rules (creating a public Activity)
1. Explicitly set the "exported" attribute to "true": exported="true"
2. Verify the received Intent and handle it in a secure manner
3. Do not include sensitive information into the resulting Intent
AndroidManifest.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.mobix.android.activity.publicactivity" >
<application
android:allowBackup="false"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
<!-- Public Activity -->
<!-- *** 1 *** Explicitly set the "exported" attribute to "true" -->
<activity
android:name=".PublicActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:exported="true">
<!-- Define an intent filter to receive an implicit Intent for a specified action -->
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.mobix.android.activity.MY_ACTION" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>PublicActivity.java
package com.mobix.android.activity.publicactivity;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class PublicActivity extends Activity {
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
// *** 2 *** Verify the received Intent and handle it in a secure manner
// Since this is a public Activity, there is a possibility that the Intent is sent by a malicious application
// See section "Secure Handling of the Input Data"
String param = getIntent().getStringExtra("PARAM");
Toast.makeText(this, String.format("Received param: \"%s\"", param), Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
public void onReturnResultClick(View view) {
// *** 3 *** Do not include sensitive information into the resulting Intent
// Since this is a public Activity, there is a possibility that the Intent will be received by a malicious application
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.putExtra("RESULT", "Not Sensitive Info");
setResult(RESULT_OK, intent);
finish();
}
}Rules (using a public Activity):
1. Do not include sensitive information into the Intent used for launching an Activity
2. Verify the received resulting data and handle it in a secure manner
PublicUserActivity.java
package com.mobix.android.activity.publicuser;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.ActivityNotFoundException;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class PublicUserActivity extends Activity {
private static final int REQUEST_CODE = 1;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
}
public void onUseActivityClick(View view) {
try {
// *** 1 *** Do not include sensitive information into the Intent used for launching an Activity
Intent intent = new Intent("org.jssec.android.activity.MY_ACTION");
intent.putExtra("PARAM", "Not Sensitive Info");
startActivityForResult(intent, REQUEST_CODE);
} catch (ActivityNotFoundException e) {
Toast.makeText(this, "Target activity not found.", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
}
@Override
public void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, Intent data) {
super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data);
// *** 2 *** Verify the received resulting data and handle it in a secure manner
// See section "Secure Handling of the Input Data"
if (resultCode != RESULT_OK) return;
switch (requestCode) {
case REQUEST_CODE:
String result = data.getStringExtra("RESULT");
Toast.makeText(this, String.format("Received result: \"%s\"", result), Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
break;
}
}
}
Also, be very careful when using an implicit Intent
|
Note! The following scenario is possible: there is no application on a user's device that can answer the implicit Intent sent by you to the |